Passare da 0 a 60 riguarda principalmente l'acceleratore, il motore, la trasmissione o il differenziale e le gomme di un veicolo. La velocità con cui ci vuole dipende dalle caratteristiche di queste parti. Quando premi il pedale dell'acceleratore/acceleratore sul tuo veicolo, ci sono un certo numero di forze in gioco per farlo funzionare.
Ecco un riassunto di base di ciò che accade quando il tuo veicolo accelera.
1.) Acceleratore al motore
Il pedale dell'acceleratore/acceleratore è una linea diretta con il motore del tuo veicolo. Controlla il flusso d'aria nel collettore di aspirazione attraverso un corpo farfallato per l'iniezione di carburante o un carburatore. Quest'aria viene quindi miscelata con il carburante, alimentato da un condotto del carburante e iniettori di carburante, o da un carburatore, e quindi viene introdotta con una scintilla (come il fuoco), alimentata da candele. Ciò provoca la combustione, che costringe i pistoni del motore a ruotare l'albero motore. Man mano che il pedale dell'acceleratore si avvicina al pavimento (tutto acceleratore in caso di moto), più aria viene aspirata nel collettore di aspirazione per essere miscelata con ancora più carburante per ruotare più velocemente l'albero motore. Questo è il "giri di giri" del tuo motore all'aumentare dei giri al minuto (rpm) dell'albero motore.
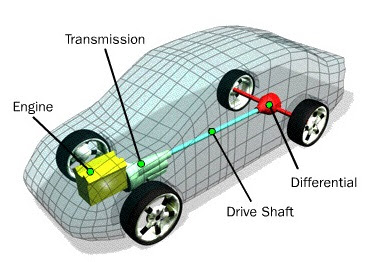
2.) Motore alla trasmissione
Se l'albero di uscita dell'albero motore di un motore non è collegato a nulla, semplicemente girerà su giri e farà rumore, non accelerazione. È qui che entra in gioco una trasmissione, poiché aiuta a trasformare la velocità del motore in velocità della ruota. Indipendentemente dal fatto che tu abbia una trasmissione manuale o automatica, entrambe le varietà attingono al motore tramite un albero di ingresso. Stretta tra il motore e la trasmissione c'è una frizione per le trasmissioni manuali o un convertitore di coppia per le automatiche. In sostanza, una frizione innesta il motore dalla trasmissione, mentre un convertitore di coppia mantiene la connessione ma utilizza uno statore unidirezionale alimentato a fluido e una turbina per eliminare lo stallo del motore al minimo. Pensalo come un dispositivo che "slitta" costantemente la connessione tra il motore e la trasmissione.
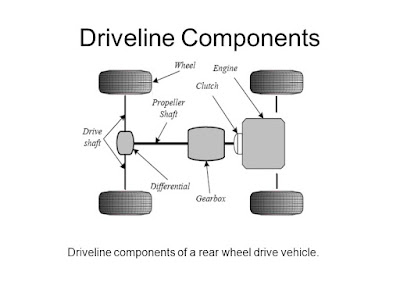
E dalla trasmissione il moto passa alle gomme in caso di moto tramite catena o cinghia e in caso di auto andrà al differenziale e da differenziale andrà alle gomme
Going from 0 to 60 mainly involves the throttle, engine, transmission or differential, and tires of a vehicle. How fast it takes depends on the features of these parts.When you hit the gas pedal/throttle on your vehicle, there are a number of forces at play to get it going.
Here is a basic run-down of what happens when your vehicle accelerates.
1.)Throttle to engine
The throttle pedal/throttle is a direct line to your vehicle’s engine. It controls the airflow into the intake manifold either through a throttle body for fuel injection, or a carburetor. This air is then mixed with fuel, fed either by a fuel rail and fuel injectors, or a carburetor, and is then introduced with spark (such as fire), fed by spark plugs. This causes combustion, which forces the engine’s pistons down to rotate the crankshaft. As the throttle pedal gets closer to the floor(full throttlr in case of motorbikes), the more air is sucked into the intake manifold to be mixed with even more fuel to rotate the crankshaft faster. This is your engine “revving” as the revolutions per minute (rpm) of the crankshaft increase.
2.)Engine to transmission
If an engine’s crankshaft output shaft is not connected to anything, it will simply rev and make noise - not acceleration. This is where a transmission comes into play, as it helps transform engine speed into wheel speed. Regardless of whether you have a manual or an automatic transmission, both varieties tap into the engine via an input shaft. Sandwiched between the engine and the transmission is either a clutch for manual transmissions, or a torque converter for automatics. In essence, a clutch and engages the engine from the transmission, while a torque converter maintains the connection but uses a fluid-fed one-way stator and a turbine to eliminate engine stalling when idle. Think of it as a device that is constantly “slipping” the connection between the engine and the transmission.
And from transmission the motion goes to tyres in case of motorbikes through chain or belt and in case of cars, it will go to differential and from differential it will go to tyres

- Log in to post comments